
I converted the assignment_data dataframe into a data table using the setDT() function from the data.table package, as shown in the Module 9 instruction. The setDT() function is widely used among R users for generating tables from dataframes, offering faster and more efficient data manipulation. This conversion keeps the original values intact while enhancing processing speed, making it especially useful for larger datasets.
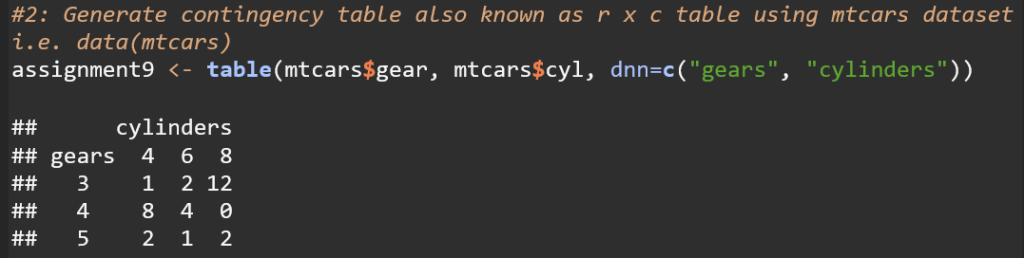
This code creates a contingency table that displays the frequency distribution of the number of cars with different combinations of gears and cylinders in the mtcars dataset.

This code adds a sum row/column that displays the sum of each of the rows and columns.
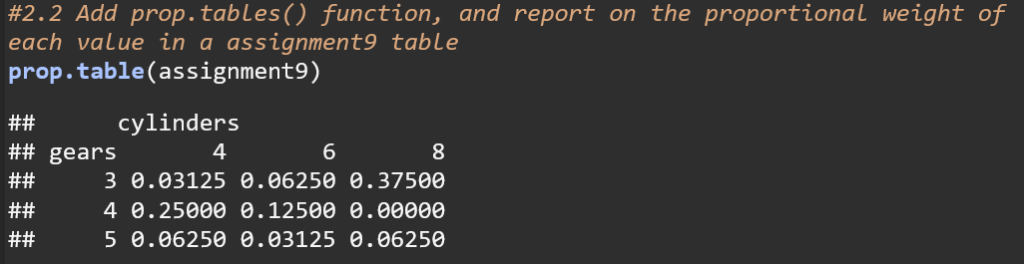
This code converts the frequency distribution table to a proportion table, showing the proportion of each element in regards to the entire dataset. For example, 3% of the cars in the mtcars dataset have 4 cylinders and 3 gears while 37.5% of cars have 8 cylinders and 3 gears.
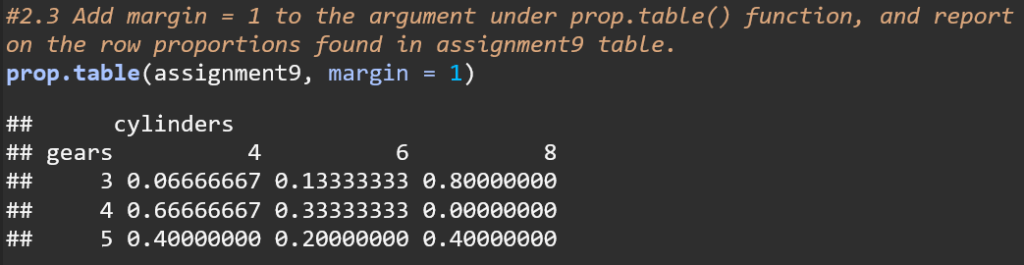
The code uses the argument margin = 1 to calculate row proportions for the assignment9 table. This means that each row’s values are shown as proportions of the total for that row. For instance, in the row for 3 gears, 66.67% of the cars have 4 cylinders, 13.33% have 6 cylinders, and 80% have 8 cylinders. This approach normalizes each row, making the sum of proportions in each row equal to 1.
Leave a comment